Solution to the Dark Matter question
Introduction:
In the late 1970’s Vera Rubin was observing galaxies and noticed that the stars in galaxies were rotating around the center of the galaxies at a constant rate. This confused astronomers who expected that the stars in the galaxies should be rotating at different speeds. In order to explain their observations astronomers came up with the concept of Dark Matter.
The reason that the galaxies are behaving as they are is not do to unseen matter and is not due to an unknown force of gravity. The real reason that the galaxies are behaving like they are is quite complex. The purpose of this article is to explain what is really going on.
Gravitational Force:
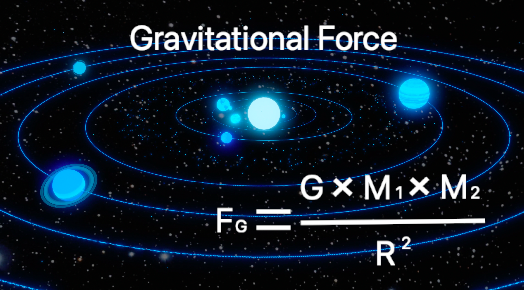
Let’s start by having a look at the two main forces involved in this phenomena. The first force is call gravitational force. This is the force that pulls object in our universe together. For example when a planet is rotating around a star, gravitational force is pulling the planet and the star towards each other.
Centripetal Force:
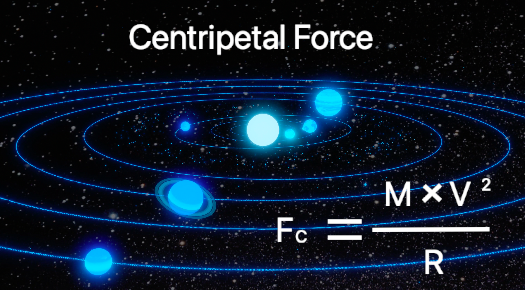
Centripetal force is a force that makes a body follow a curved path. For the context of this article it is used to describe the force that counter acts gravitational force. Basically it is the force that causes an object rotating around a central point to pull away from the central point.
Stable Orbit:

In order for a planet revolving around a star to have a stable orbit the two main forces acting upon it need to be the same. This means that in order for an orbit to be stable, gravitational force and centripetal force need to equal each other. If not the orbiting object will move towards or away from the center.
Tangential Velocity:

In order to understand why the galaxies are behaving like they are it is necessary to understand the concept of tangential velocity. This is basically the speed of an object that is rotating around a central point. In this article orbital speed and speed will also be used to refer to tangential velocity.
Increasing Distance:
Traditional Interpretation

The factor of distance effects gravitational force and centripetal force differently. The deviation between the two forces causes something interesting to happen. In order to keep a stable orbit as the distance of an object from the central point increases, the tangential velocity of the object needs to be reduced.
This means that the speed of a stable orbiting object decreases as the distance from the central point increase. This is a true fact and is a commonly known phenomena that physicists and astronomers understand. It is also the reason why astronomers expect that the stars rotating around the center of a galaxy should be rotating at different speeds depending on their distances from the center.
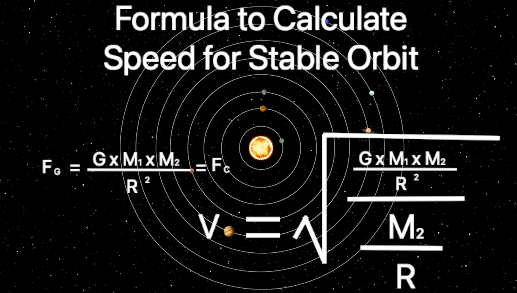
The Formula:
In order to explain what astronomers are observing we need a formula that calculates the required tangential velocity in order to maintain a stable orbit. It is necessary to combine the gravitational force equation and the centripetal force equation, solve for tangential velocity and use distance as the variable.
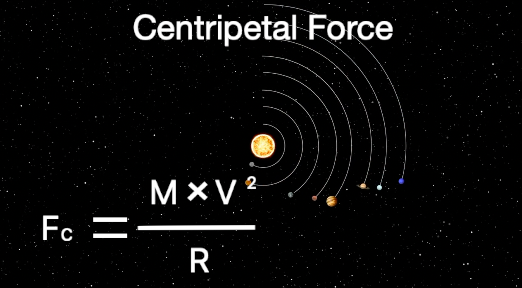
First we need solve for V or tangential velocity:
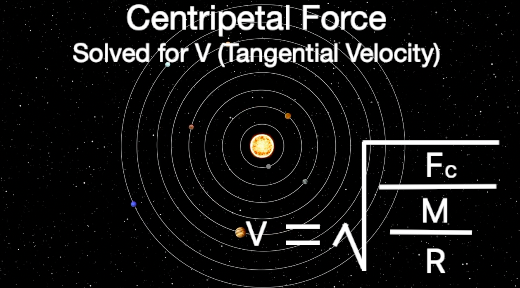
Finally we replace centripetal force with the formula for gravitational force. This formula will allow us to calculate the speed (Tangential Velocity) required to maintain a stable orbit. We will use this formula to create a model that will help explain why galaxies are behaving like they are.
Increasing Distance:
Modern Interpretation
The difference in speed is too small to observe.
When astronomers observe galaxies they expect to observe that the stars in galaxies rotate at different speeds according their distance from the center. The reason is that when they observe solar systems this is what they see.
Their observations however do not reflect this. Instead the stars appear to be moving at the same speed. Their explanation as to why their observations do not fit their expectations is that dark matter is causing the galaxies to behave differently as they should be behaving.
The reality is that the galaxies are not behaving wrong or strangely. The problem is that the astronomer’s expectations are incorrect. The reason for this is that the laws of gravitational force and centripetal force work differently on different scales. When observing galaxies the difference in speed is so small that it can not be observed.
Model:

This model was created to demonstrate why the difference in speed is so small. It is based on a star with a planet orbiting around it at different distances and speeds.
It shows that the speed of orbit decreases as distance increases as expected, but there is also something else going on. As distance increases the decrease in speed necessary to maintain a stable orbit decreases.
The example planet must travel 1,784 kilometers an hour in order to have a stable orbit at 150,000,000 kilometers away from the star. If the planet’s orbit would be increased by 150,000,000 kilometers then the necessary speed to have a stable orbit would be 1,262 k/h. The decrease in speed would therefore be 522 k/h.
As we increase distance the reduction of orbital speed needed to keep a stable orbit decreases. For example if we increase the distance to 1,350,000,000 kilometers the speed required to keep a stable orbit would be 594 k/h. At this distance an increase of 150,000,000 kilometers would require the speed to be reduced to 564 k/h. The reduction of orbital speed needed to maintain a stable orbit is only 30 k/h. To put this into perspective, Saturn is 1,500,000,000 kilometers from the sun.
The need for a reduction in tangential velocity decreases exponentially as distance increases or the need for a decrease of the orbital velocity decreases towards infinity as distance increases.
Galaxies:

Galaxies are really big, the distances are enormous and hard to comprehend. As the distance of stars from the center of their galaxies increases the difference of their orbital speed reduces to the point that it is not observable with our instruments. Because of scale of galaxies the point at which this happens is relatively close to the center of galaxies. As a result all the stars orbiting around the centers of galaxies appear to be moving at the same speed.
The Sun:
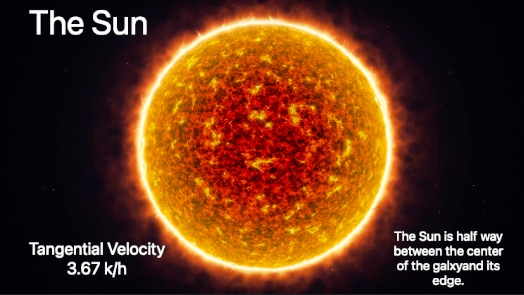
A good example would be the sun. It is located about half way between the center of our galaxy and its observable edge. The sun’s tangential velocity is estimated to be 220 k/s or 3.67 k/h. According to the laws of physics the stars farther away than the sun should have slower orbital speeds. The reduction in speed however should not exceed 3.67 k/h.
This means that the speed difference between all the stars from the sun’s orbit to the edge of the galaxy should be less than 3.67 k/h. This deviation is too small to observe when are observing galaxies. This is why all the stars seem to be rotating around galaxies at the same speed when we observe them.
Conclusion:

When we observe galaxies all the stars appear to be moving at the same speed. Astronomers expect that the stars on the edge of the galaxies are moving too fast. As a result they should be flying out of the galaxies.

Astronomers believe that the reason that this happens is because the galaxies have much more matter than we expect. When we observe galaxies we can not see this matter. This would mean that we could not see most of the matter in galaxies. The explanation for this is that there must be dark matter in the galaxies that we ca not see.

The reality is that the reason that the stars in galaxies seem to be revolving around their centers at the same speed is that they are following the laws of physics. The expected reduction in speed can not be observed because it is so small. Astronomers have failed to take into consideration the vast distances between the stars in galaxies. These distances result in the need for a reduction in speed to keep a stable orbit to be very small. So small it can not be observed.

When an orbiting object moves farther from its center the orbital speed must be decreased in order to maintain a stable of orbit. The reason for this is that calculations for gravitational force and centripetal force use distance differently. This difference is reduced exponentially as distance from the center increase. This means that the required speed reduction to maintain a stable orbit is only observable when the distance from the center is relatively small. Galaxies are so large that the speed reduction required to maintain a stable orbit is so small that it can not be observed.


No responses yet